Understanding Migraine With and Without Aura

Anyone who has ever had a throbbing headache that seems to take over the entire day is not alone. Migraines affect millions worldwide and they come in more than one form. Although many people recognise the typical migraine, fewer are aware that there are two primary types: migraine with aura and migraine without aura. Knowing the difference between the two can help in managing migraines better and possibly reduce their occurrence.
Migraine Without Aura
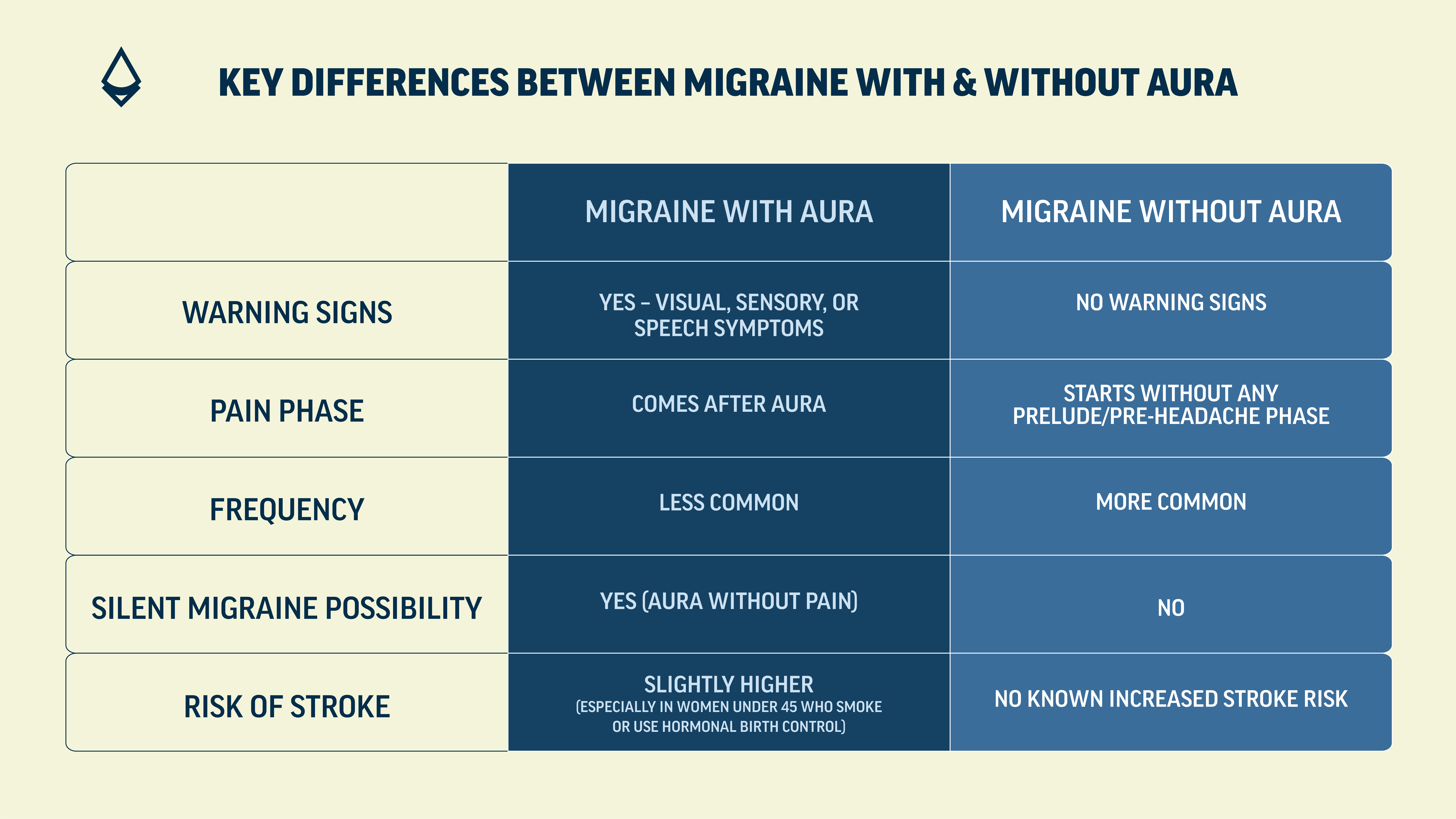
Also known as common migraine, this type comes without any warning. The pain starts suddenly, often on one side of the head, and can last anywhere from 4-72 hours. With this type of migraine, there are no signals or indicators of an incoming migraine, which makes it unpredictable and hard to catch early.
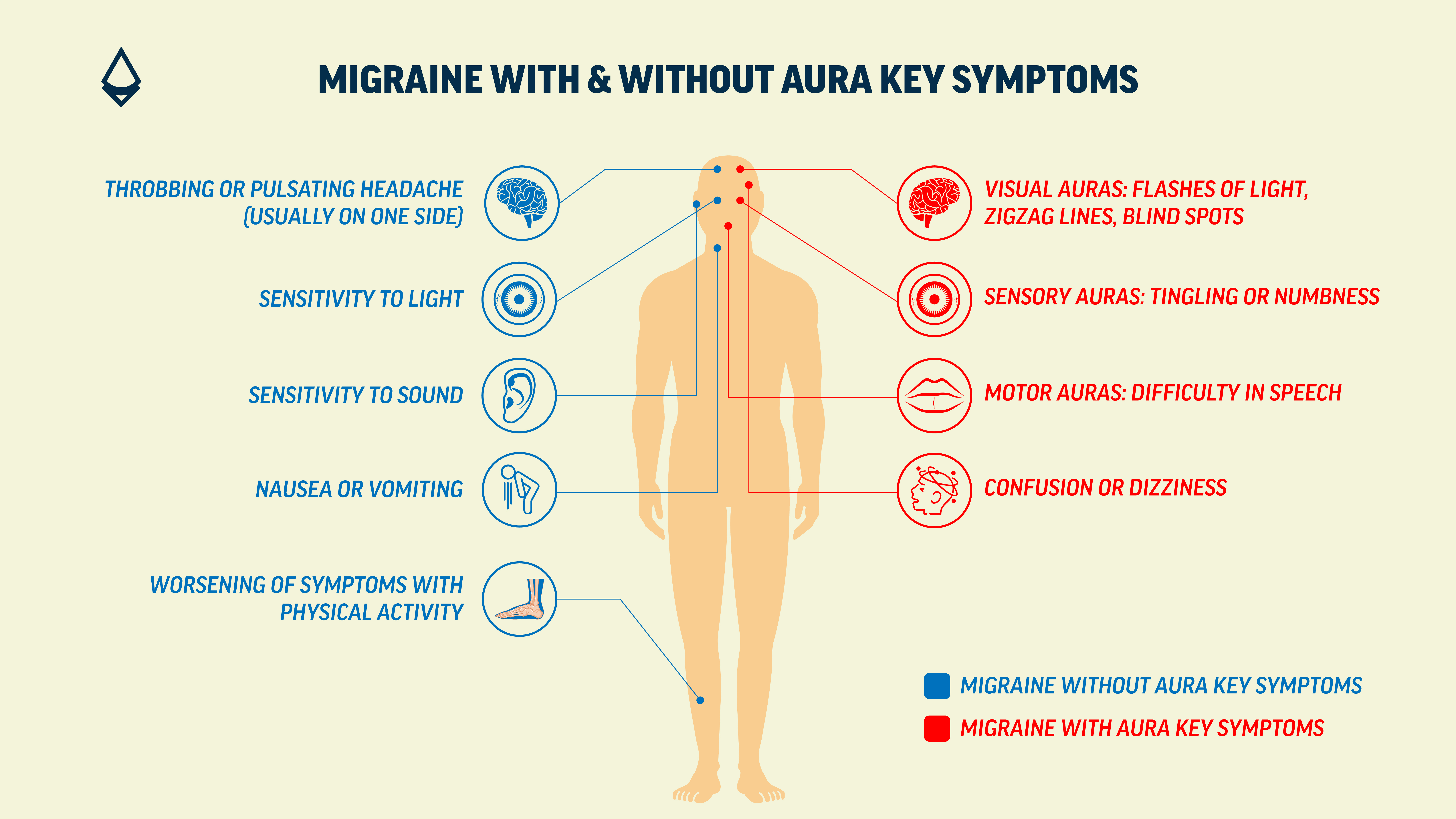
Key Symptoms Include:
Throbbing or pulsating headache (usually on one side)
Sensitivity to light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia)
Nausea or vomiting
Worsening of symptoms with physical activity
Migraine With Aura
A migraine with aura, also known as a classic migraine, includes a set of neurological symptoms that come before the headache phase. This aura typically develops gradually over 20–60 minutes and fades before or as the headache begins. Not everyone with migraine with aura has all the symptoms, and sometimes the aura happens without a headache. This is called a silent migraine.
Key Symptoms Include:
Visual Auras: Visual changes such as flashes of light, zigzag lines, blind spots
Sensory Auras: Changes like tingling or numbness, usually starting in one hand and moving up the arm or to the face
Motor Auras: Difficulty in speech, including trouble finding words or slurred speech
Confusion or dizziness
What Causes the Aura?
The exact cause of auras in migraine isn't fully understood, but researchers believe it may be linked to a slow wave of altered brain activity, known as cortical spreading depression. This wave causes temporary changes in brain chemicals, nerve activity, and blood flow, which can affect how the brain functions and may trigger the migraine pain that follows.
As this wave spreads, it disrupts the brain's electrical and vascular balance, possibly activating pain-sensitive pathways and inflammation. By studying these processes, scientists hope to identify precise targets in the brain that can be blocked or stabilised, which can further pave the way for new treatments that could stop migraines before they start.
Most people with migraines get migraines without aura. Only about 25–30% experience aura. Interestingly, someone who gets migraines with aura won’t always have an aura every time, they might have both types at different times in life.
Can One Type of Migraine Turn Into the Other?
Yes, it’s possible. Some people who initially have migraine without aura may develop aura later in life and vice versa. Changes in hormones, lifestyle, medications, or even brain chemistry can influence how migraines show up.
Managing Migraines With and Without Aura
While both types of migraines can be managed similarly, understanding the specific pattern helps in recognising early warning signs and avoiding triggers.
Managing migraines, whether with or without aura, starts with spotting migraine triggers and maintaining a steady routine. Keeping track of food, sleep cycle and weather can reveal patterns we might miss otherwise. Sticking to regular meals, staying hydrated, and getting consistent sleep can help prevent attacks. When a migraine starts, limit screen time, avoid bright lights, and rest in a quiet, dark room. Some people also find relief using a cold compress.
Natural Ways to Manage Migraine With and Without Aura
Certain supplements and therapies can help reduce migraine frequency, especially for those with aura. Magnesium from leafy greens, bananas, nuts and riboflavin, also known as Vitamin B2, has shown promise when taken regularly. Stress-reducing practices like yoga and mindfulness can help prevent attacks, while acupuncture may lower migraine days for some. Cannabinoid-based medication has the potential to reduce pain and inflammation, offering a natural option under medical guidance. If someone starts experiencing new aura symptoms, especially changes in vision, speech, or sensation, it is important to consult a healthcare expert.
Final Thoughts
Migraines, with or without aura, are not just headaches; they are neurological events with distinct patterns and symptoms. Identifying whether a person experiences an aura can help with early preparation, timely action, and even prevention of some attacks. Through lifestyle changes, tracking triggers, or exploring natural remedies, understanding the type of migraine is a key step toward more effective management.